Understanding Electronic Health Information (EHI)
EHI is part of the information blocking definition. An actor subject to the information blocking regulations could be found to have committed information blocking if the actor engages in a practice that is likely to prevent, or materially discourage, or otherwise inhibit (interfere with) the access, exchange, or use of EHI.
What is EHI?
EHI is electronic protected health information (ePHI) to the extent that it would be included in a designated record set (DRS) (other than psychotherapy notes or information compiled in reasonable anticipation of, or for use in, a civil, criminal, or administrative action or proceeding), regardless of whether the group of records is used or maintained by or for a HIPAA covered entity.
How does the EHI definition align with HIPAA healthcare terminology?
The EHI definition incorporates terms defined in the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) and the HIPAA Rules that are used in the healthcare industry. It focuses on a set of health information that HIPAA covered entities and business associates currently collect, maintain, and make available for access, exchange, and use. For example, EHI is a subset of the same information (i.e., the Designated Record Set) that covered entities must make available for patients to access when they exercise their HIPAA right of access.
What is the relationship between EHI and other healthcare terminology (HIPAA terms and the USCDI)?
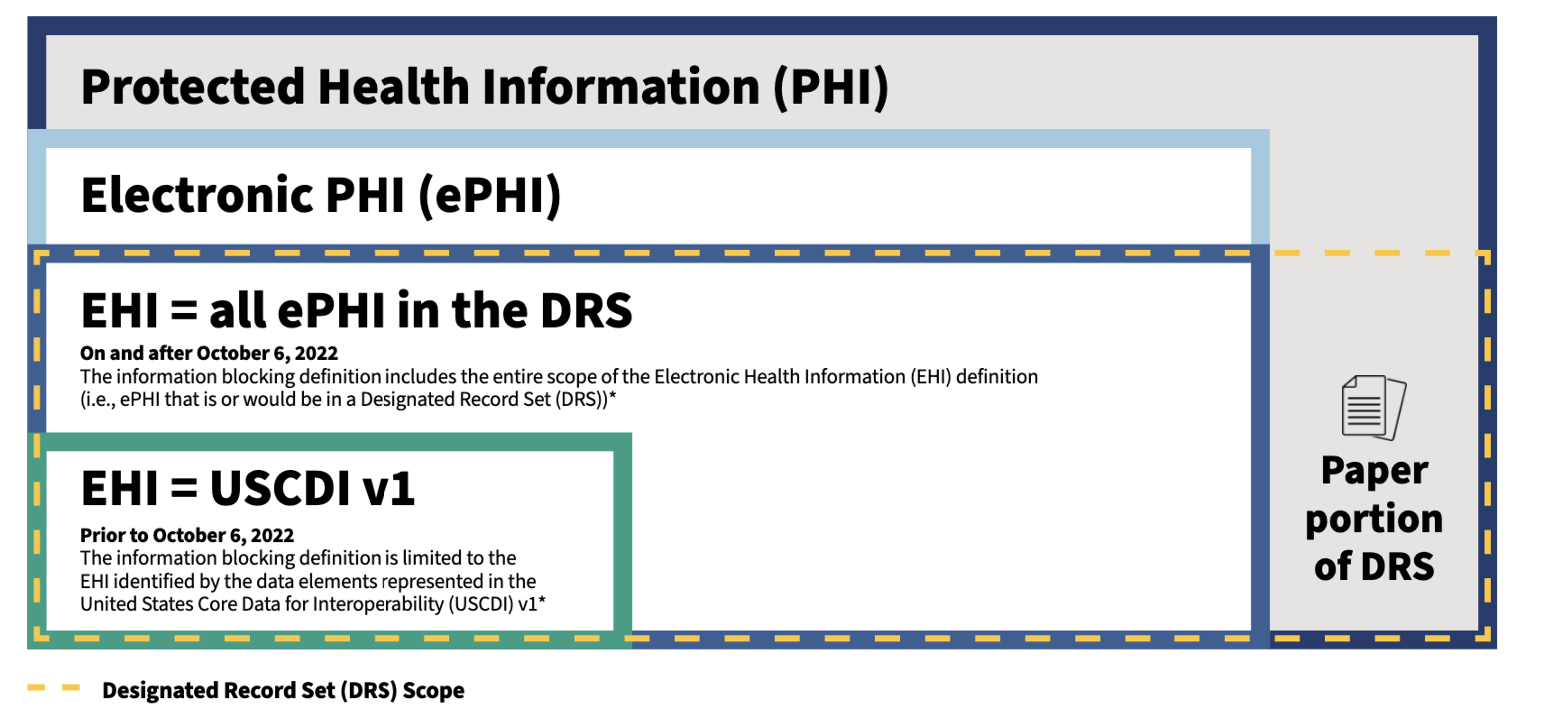
We have created a graphic that shows the relationship between EHI and other relevant healthcare terminology.

EHI includes electronic protected health information (ePHI) to the extent that it would be included in a designated record set (DRS), regardless of whether the group of records is used or maintained by or for a covered entity or business associate. EHI does not include: psychotherapy notes as defined in 45 CFR 164.501; or information compiled in reasonable anticipation of, or for use in, a civil, criminal, or administrative action or proceeding. 45 CFR 171.102
The graphic is not intended to depict the actual scope of each category of health information in a designated record set. For example, a DRS may consist of no paper records and EHI identified by only the data elements represented in the USCDI v1.
Actors (45 CFR 171.102) not covered by HIPAA should familiarize themselves with this infographic and with HIPAA terms, and should assess what information they have that would be considered records that align with those included in the DRS. Such information is EHI for purposes of the information blocking definition.
Before October 6, 2022, electronic health information (EHI) for the purposes of the information blocking definition is limited to the EHI identified by the data elements represented in the United States Core Data for Interoperability (USCDI) v1. On and after October 6, 2022, the information blocking definition will apply to the full scope of EHI (as defined in 45 CFR 171.102).
How to Determine if Information is EHI
To determine whether the information is EHI, consider the following:
If the information
-
Is individually identifiable health information that is:
Maintained in electronic media
Transmitted by electronic media
and
-
Would be included in one of the following groups of records:
- medical records and billing records of a provider about individuals;
- enrollment, payment, claims adjudication, and case or medical management record systems maintained by or for a health plan;
- records used in whole or in part, to make decisions about individuals
and
-
Is not excluded from the EHI definition (see exclusions listed below)
Then it is EHI


